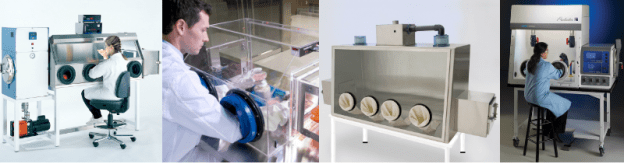
What Is a Glove Box?
Sometimes a controlled environment becomes a necessity during the performance of experiments or the handling of certain materials. When this happens, a special device, called an isolation glove box, allows researchers to perform their tasks with materials kept in strict isolation. The positive-pressure box shields materials from damaging environmental elements such as moisture.
But what exactly is a glove box? As its name suggests, it is a sealed box manufactured using materials such as acrylic, static-dissipative PVC or stainless steel that includes two or more gloves, used to handle the contents within. While there are several types of glove boxes, the basic premise behind them all is the same…to give the user the ability to handle substances or objects without breaking strict isolation protocols.
The two main types of glove boxes are “Isolation” and “containment.” The difference depends on what needs protection: the sample inside, or the environment outside. Isolation boxes contain positive pressure; the surplus insert gas is expelled out into the room through valves. Containment boxes are negative pressure – the air must be vented to the outside, or through a filter due to processing hazards created inside (fumes, vapors, dust).
Glove boxes are a common sight in many scientific facilities, mainly in the medical and research fields, but can also be found in unexpected environments. For example, a mobile glove box was included on the Mir space station, where hundreds of specially designed experiments were carried out.
The History of the Glove box: What, Why, When and Where?
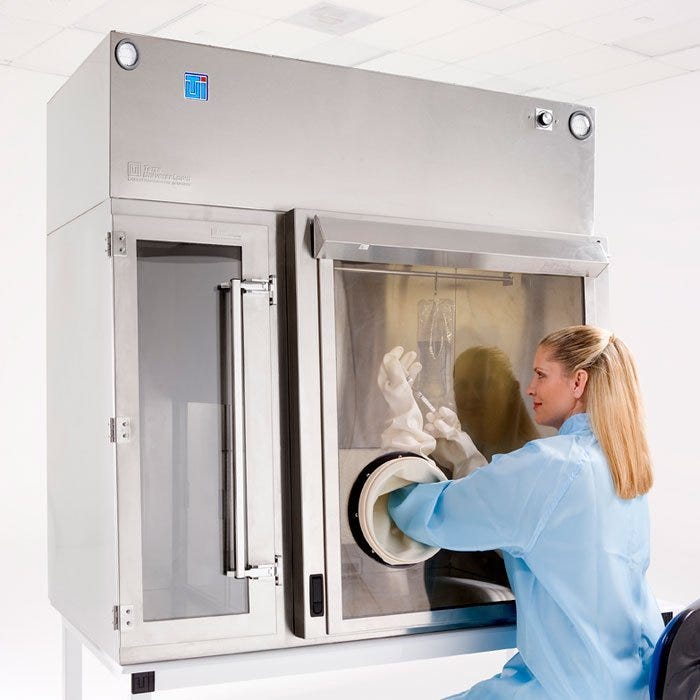

Glove boxes have been in use in one form or another since the 1940s, when they became a permanent fixture in military facilities where research was carried out with radioactive materials. In those days, they were crafted out of steel with only a small viewing window and even smaller glove ports, which reduced the user’s risk of exposure to the materials contained in the containment unit. Glove ports have since been enlarged and improved to allow for more freedom of movement during use.
The special containment characteristics provided by glove boxes became popular in the years following World War II, when they became more commonly used in the medical research field. It was found that glove boxes could be used effectively in the handling of viruses and other pathogens for the creation of vaccines and pharmaceuticals. Isolation glove boxes went on to become very popular during the late 1960s and 1970s when NASA employed them to handle and study rocks brought back from the moon to avoid any cross contamination with any pollutants in the Earth’s atmosphere.
These days, isolation glove boxes are used everywhere from the electrical industry as a way to avoid static contamination to hospital nurseries, where premature babies now have a higher chance of survival thanks to the strictly controlled environment they provide. From the day they first appeared on the market, glove boxes have provided their users with the ability to determine the atmosphere in which certain tasks will be carried out, which allows for safer working conditions and more reliable results.
Development and Changes through the Years

Glove boxes have evolved and improved over time; from plain steel boxes with small windows and plastic gloves to state-of-the-art transparent cases with a large variety of glove materials and types. Every glove box is built to serve different purposes, but their most basic premise remains unchanged.
With the physical changes undergone by glove boxes over the years, their purpose has expanded. While originally intended for military use and research, they are now widely accepted by a diverse range of industries, including the food industry, health care, and education departments. All industries that utilize glove boxes benefit from the high level of control they offer.
Isolation glove boxes have become an important factor in quality assessment tests, as well as experimentation under conditions that are impossible to achieve in another way. Glove boxes allow operators to create rarefied atmospheres, inert environments, and even vacuum conditions making them incidental to the success of many of the scientific advancements in the last 30 years.
Glove boxes are common additions to cleanrooms. Keeping operators safe in a cleanroom environment while operating a glove box has proved to be very efficient at preventing contamination, and is cost-effective in protecting samples that require a high level of cleanliness and safety.
Materials and Construction
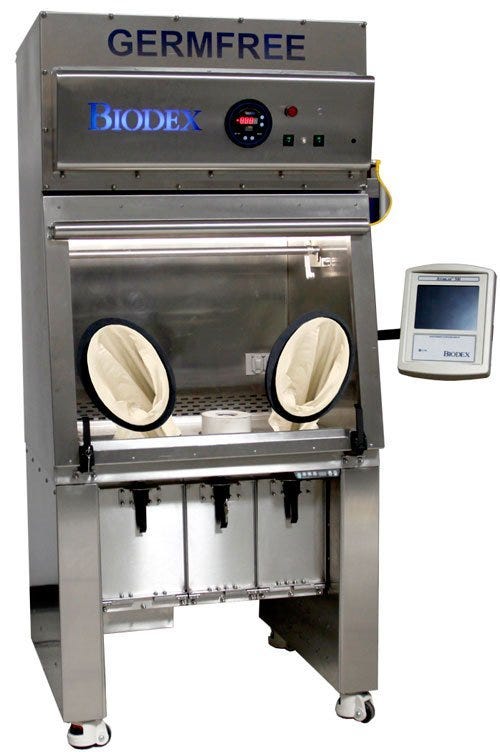 As previously mentioned, glove boxes were originally crafted out of steel, glass, plastic and rubber. But with the creation of more resistant materials, glove boxes can be constructed out of a diverse range of plastics, metals, and polymers. These include stainless steel, aluminum sheet metal, fiberglass, polyethylene, safety glass, PVC and other, more lightweight, durable, and advanced plastics.
As previously mentioned, glove boxes were originally crafted out of steel, glass, plastic and rubber. But with the creation of more resistant materials, glove boxes can be constructed out of a diverse range of plastics, metals, and polymers. These include stainless steel, aluminum sheet metal, fiberglass, polyethylene, safety glass, PVC and other, more lightweight, durable, and advanced plastics.
The specific construction of a glove box can depend on many factors, including the space in which it will be placed, the intended use, and even ergonomic factors related to its users. In this manner, we can find smaller PVC glove boxes used in space shuttles, to larger, multi-port glove boxes such as those found in pharmaceutical research facilities.
Even with all the changes made to the physical qualities of the glove box casing throughout the last few decades, the most visible evolution has occurred in the materials used to craft the gloves and sleeves of each glove box. Where once all gloves were made of plastic or rubber, today we use a wide range of materials including butyl for the prevention of static in the electronics industry, neoprene, hypalon, and nitrile which offer a high level of chemical resistance and a better fit for handling more delicate items within the enclosure.
Portable Glove Boxes
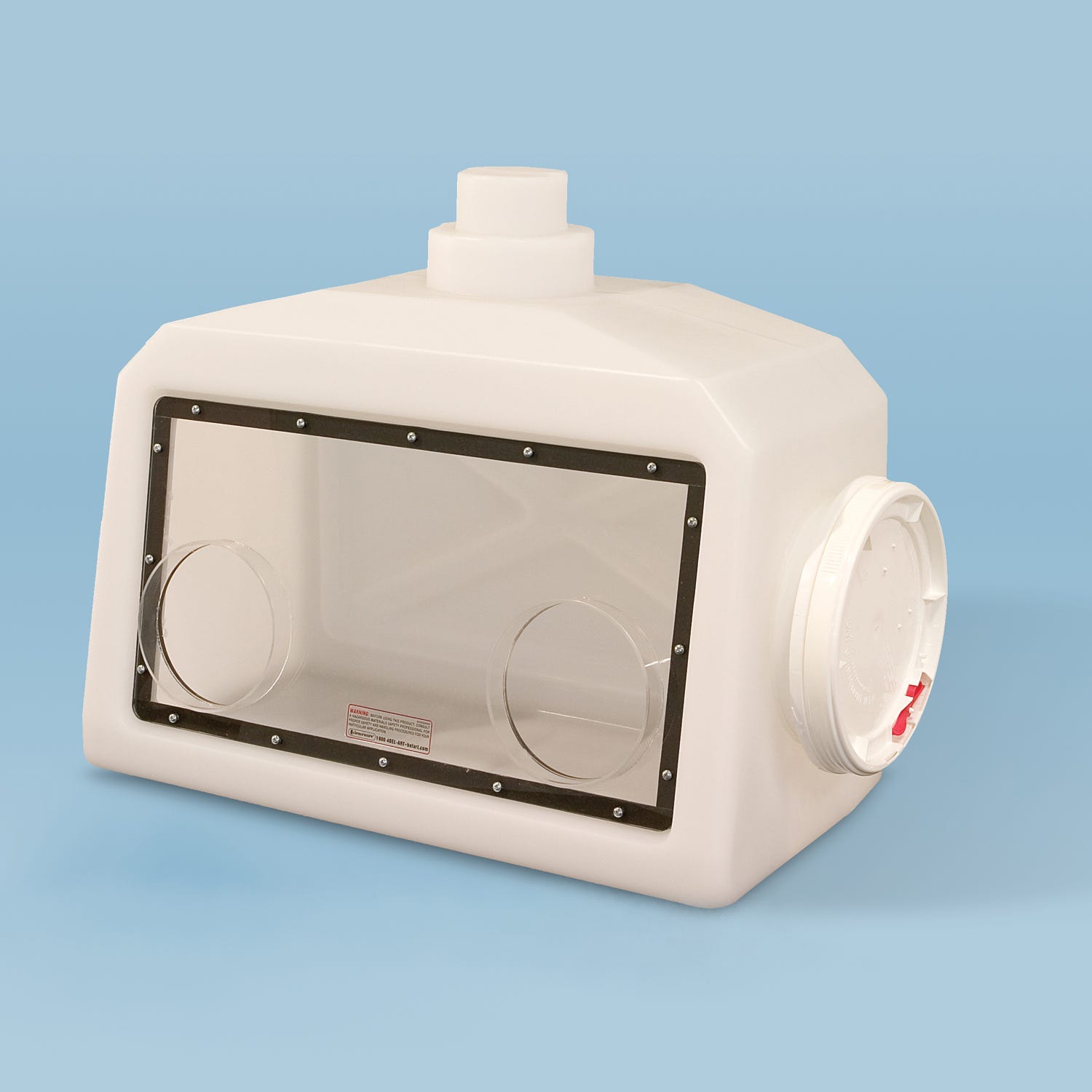

Glove boxes should ideally remain in a fixed position within a certain area, but because of their multiple applications and the new frontiers being explored each day, the need for mobility is a common occurrence in the glove box industry. Now we have access to a wide selection of portable boxes which are being used for a myriad of tasks, including hardware experimentation in outer space.
While most glove boxes are usually large and stationary, mobile devices are more streamlined and compact. They are also lighter and can be crafted out of plastic materials. Mobile glove boxes are not limited to the aerospace industry and are becoming more common in the food processing and healthcare industry, providing the user with the ability to transport its isolated environment to any desired location with very little manpower.
Present Day Applications
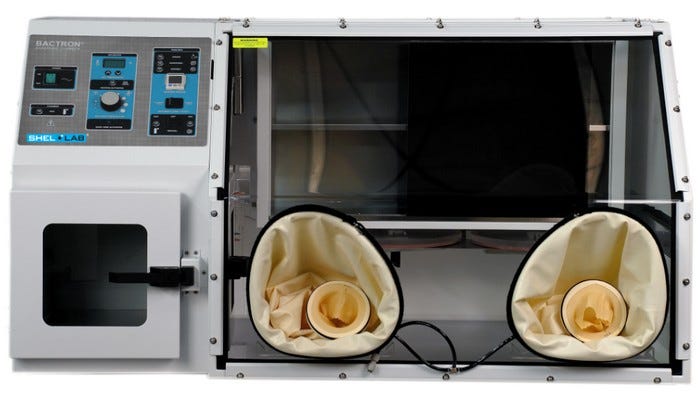

The applications for glove box technology appear to be limitless and interest in their use is growing with each passing day. From the appearance of the first glove boxes just seven short decades ago they have bloomed into a technology that knows few boundaries. At this time, glove boxes are being used for countless applications in different industries across the world.
What was once a piece of equipment limited to use by the military for radiological research has now grown into an influential factor in the improved shelf life of food products, pollution free environments, and an overall improvement of health in the world’s population. The history of the glove box has not only been interesting, it also provides us with an unexplored world of possibilities and benefits of scientific advancement in all areas of life.
Gloveboxes